BCI Vocabulary Reference
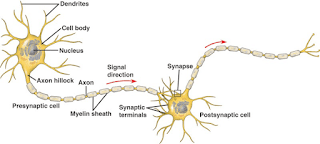
synapse: In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell. In many synapses, the presynaptic part is located on an axon and the postsynaptic part is located on a dendrite or soma.
Dipole: There are many dipoles in the brain. Each dipole will influence the charge in almost all directions. The voltage fluctuation measured at the electrode on the scalp is the sum of activities generated from many neural sources. [EEG Signal Processing and Feature Extraction, Page 25]
Dendrites and an Axon: Apart from the cell body, a typical neuron possesses several dendrites and an axon. The dendrites, extruding from the cell body, are primarily responsible for providing a large receptive area for synaptic input, thus receiving the electrical input to the cell body. The single axon, which arises from the cell body, mainly takes charge of the transmission of action potential, and provides contacts with other nerve cells by the synapses, where signals are sent from the axon of one neuron to a dendrite of another.
Elicit: To draw out
Delineation: Description with pictures
Montage: The technique of selecting, editing, and piecing together separate sections of film to form a continuous whole.
Temporal: is a fancy term referring to comparisons made with respect to the passage of time. If a process is temporally extended, it means that it happens over a period of time. ... "Spatial", on the other hand, refers to comparisons or references with respect to 3D space.
Electrocorticography (ECoG): Records signals directly from the brain. The ECoG has higher spatial resolution, broader bandwidth, higher amplitude, and less sensitivity to artifacts such as electromyographic (EMG) signals. ECoG signals are captured through placing a number of electrodes under the skull.
Information Transfer Rate (ITR):
EOG: Electrooculography
EMG: Electromyography
Morphologies: The study of the forms of things
Frontalis Muscle:
Temporalis Muscle:
Ambulatory:
Common Spatial Pattern (CSP):
Independent Component Analysis (ICA):
Common Average Reference (CAR):
Surface Laplacian:
Filter Bank Common Spatial Patterns (FBCSP):
Mutual Information (MI):
Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA):
𝑘-nearest neighbors (kNN):
Support Vector Machines with linear (SVMLIN) and radial basis function (SVMRBF) kernels:
Random Forest (RF)
Artificial Neural Networks (NN):
Seizure:
Higher Order Crossings:
Fractal Dimensions:
Dipole: There are many dipoles in the brain. Each dipole will influence the charge in almost all directions. The voltage fluctuation measured at the electrode on the scalp is the sum of activities generated from many neural sources. [EEG Signal Processing and Feature Extraction, Page 25]
Dendrites and an Axon: Apart from the cell body, a typical neuron possesses several dendrites and an axon. The dendrites, extruding from the cell body, are primarily responsible for providing a large receptive area for synaptic input, thus receiving the electrical input to the cell body. The single axon, which arises from the cell body, mainly takes charge of the transmission of action potential, and provides contacts with other nerve cells by the synapses, where signals are sent from the axon of one neuron to a dendrite of another.
Elicit: To draw out
Delineation: Description with pictures
Montage: The technique of selecting, editing, and piecing together separate sections of film to form a continuous whole.
Temporal: is a fancy term referring to comparisons made with respect to the passage of time. If a process is temporally extended, it means that it happens over a period of time. ... "Spatial", on the other hand, refers to comparisons or references with respect to 3D space.
Electrocorticography (ECoG): Records signals directly from the brain. The ECoG has higher spatial resolution, broader bandwidth, higher amplitude, and less sensitivity to artifacts such as electromyographic (EMG) signals. ECoG signals are captured through placing a number of electrodes under the skull.
Information Transfer Rate (ITR):
EOG: Electrooculography
EMG: Electromyography
Morphologies: The study of the forms of things
Frontalis Muscle:
Temporalis Muscle:
Ambulatory:
Common Spatial Pattern (CSP):
Independent Component Analysis (ICA):
Common Average Reference (CAR):
Surface Laplacian:
Filter Bank Common Spatial Patterns (FBCSP):
Mutual Information (MI):
Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA):
𝑘-nearest neighbors (kNN):
Support Vector Machines with linear (SVMLIN) and radial basis function (SVMRBF) kernels:
Random Forest (RF)
Artificial Neural Networks (NN):
Seizure:
Higher Order Crossings:
Fractal Dimensions:
Hilbert-Huang Spectrum:
(M)ANOVA: Multivariate Analysis of Variance
mRMR: minimum-redundancy maximum-relevancy - feature section method
Naive Bayes classifier:
Intrinsic mode functions:
Confusion Matrix:
Database for Emotion Analysis using Physiological data (DEAP):
Confusion Matrix:
Hjorth parameters:
Caveat: warning, conditions or limitations
Rapid Serial Visual Presentation (RSVP):
Event Locked:
Phase Locked:
Orthonormal: Vectors are one unit long and perpendicular to each other.
Orthogonal:
Singular Value Decomposition:
Superdiagonal Tensor:
Rapid Serial Visual Presentation (RSVP):
Event Locked:
Phase Locked:
Orthonormal: Vectors are one unit long and perpendicular to each other.
Orthogonal:
Singular Value Decomposition:
Superdiagonal Tensor:



Comments
Post a Comment